Definition, Explanation and Examples

CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI roadshow australia 2020 exhibitors has compiled many resources to assist you along the path. In other words, all assets initially come from liabilities and owners’ contributions.
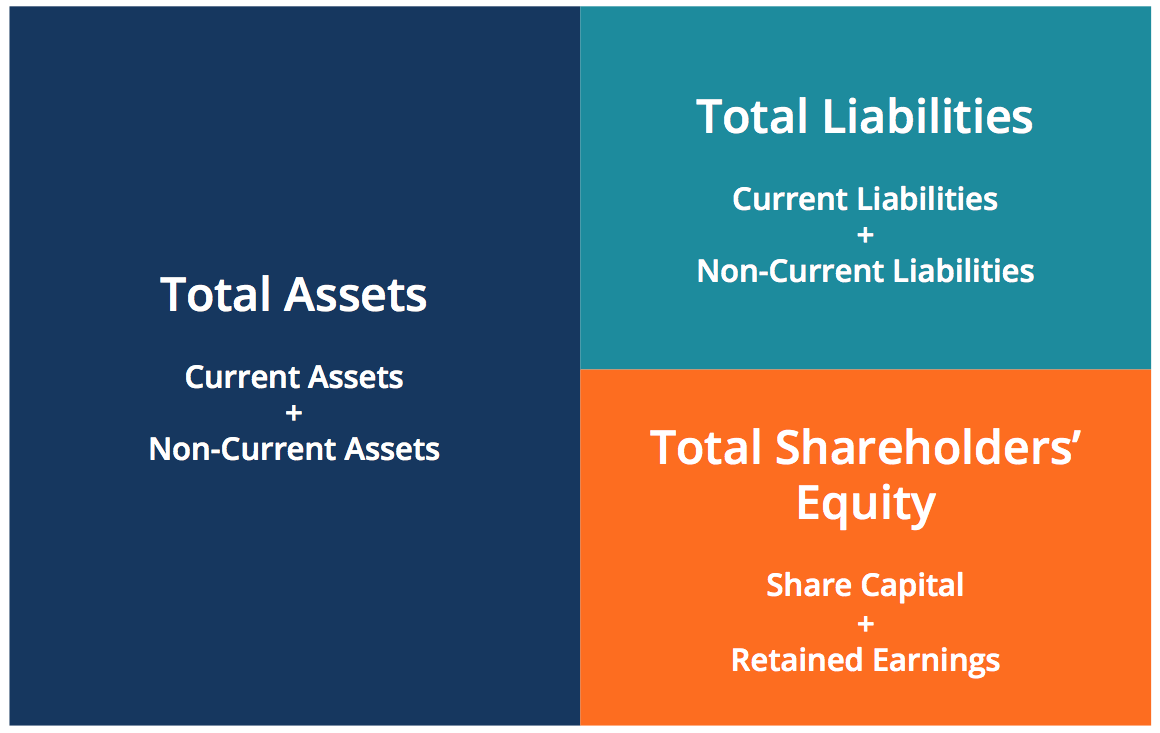
Assets, Liabilities, And Equity
If the net amount is a negative amount, it is referred to as a net loss. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry accounting system. Every financial transaction impacts at least two accounts, maintaining the balance. Anushka will record revenue (income) of $400 for the sale made.
A company has liabilities of $25,000 and assets of $35,000. What is the company’s equity?
Liabilities can also be classified as current or non-current. A liability is considered current of they are payable within 12 months from the end of the accounting period, or within the company’s normal operating cycle if the cycle exceeds 12 months. The accounting equation is a vital concept in accounting, underpinning financial reporting and analysis. Understanding it is crucial for anyone involved in finance. Cash (asset) will reduce by $10 due to Anushka using the cash belonging to the business to pay for her own personal expense.
Let’s add transaction #3:
Think of retained earnings as savings, since it represents the total profits that have been saved and put aside (or “retained”) for future use. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs). CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
Effects of Transactions on Accounting Equation
So let’s discuss what each of these are and we’ll see how this is always going to be true. As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change. The accounting equation nonetheless always stays in balance. The accounting equation ensures that a company’s balance sheet remains balanced. It serves as a vital tool for financial analysis and reporting.
He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. Parts 2 – 6 illustrate transactions involving a sole proprietorship.Parts 7 – 10 illustrate almost identical transactions as they would take place in a corporation.Click here to skip to Part 7. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. The global adherence to the double-entry accounting system makes the account-keeping and -tallying processes more standardized and foolproof.
In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment. When a company purchases goods or services from other companies on credit, a payable is recorded to show that the company promises to pay the other companies for their assets. Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets. If an accounting equation does not balance, it means that the accounting transactions are not properly recorded. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity). Both sides of the accounting equation are always equal.
- The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position.
- Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets.
- Consider a company with assets totaling $100,000, liabilities of $60,000, and equity of $40,000.
- In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as owner’s equity.
In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation. Notice that each transaction changes the dollar value of at least one of the basic elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner’s equity) but the equation as a whole does not lose its balance. If the left side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation. The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity.
In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business. The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends.